241213 에이콘 아카데미 수업에 기반하여 작성되었음을 알립니다.
데이터 분석
분석
정량적 방법 (수치로 결과가 나타남, 회기가 된다.)
정성적 방법 (수치로 결과가 나오긴 한다. 0, 1 / 0, 1, 2 / 0~9 이렇게 분류되어 나온다. 분류가 된다.)
수치(숫자) / 문자, 이미지, 그림, 소리의 경우 수치화해주어야한다.
단순 선형 회기는 현실에 없다. 독립변수와 종속변수가 각각 1개뿐이기 때문이다.
여러개의 독립변수가 하나의 종속변수에 영향을 끼치는 현실 세계에는 맞지않는다.
현실 세계를 분석하려면 다중 선형 회기 분석을 해야한다.
🙏 캐글
🙏 GPU 제공 : 구글 콜랩
다중 선형 회기
tf4boston_lm2.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/@tensorflow/tfjs/dist/tf.min.js"></script>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/@tensorflow/tfjs-vis/dist/tfjs-vis.umd.min.js"></script>
<style>
#loading-message {
display: none; /* 초기에는 숨김 */
font-weight: bold;
color: #007bff;
margin: 20px 0;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
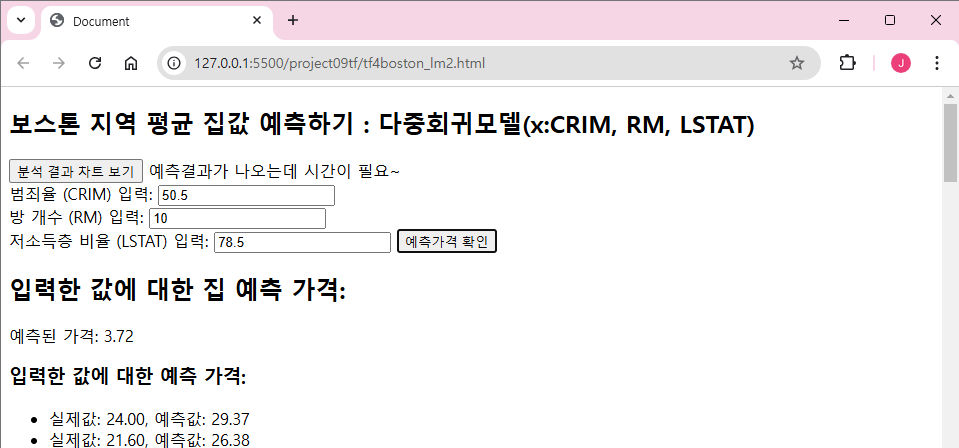
<h2>보스톤 지역 평균 집값 예측하기 : 다중회귀모델(x:CRIM, RM, LSTAT)</h2>
<button id="showButton">분석 결과 차트 보기</button> 예측결과가 나오는데 시간이 필요~
<div id="loading-message">선형회귀 모델 생성 중 ...</div> <!-- 모델 생성 중 메시지 -->
<div id="result-container" style="display: none;">
<div id="input-container">
<label for="crimInput">범죄율 (CRIM) 입력:</label>
<input type="number" id="crimInput" step="0.01" min="0" /><br/>
<label for="roomsInput">방 개수 (RM) 입력:</label>
<input type="number" id="roomsInput" min="1" /><br/>
<label for="lstatInput">저소득층 비율 (LSTAT) 입력:</label>
<input type="number" id="lstatInput" step="0.1" min="0" />
<button id="predictButton">예측가격 확인</button>
</div>
<div id="single-prediction-container">
<h2>입력한 값에 대한 집 예측 가격:</h2>
<p id="singlePrediction"></p>
</div>
<div id="predictions-container">
<h3>입력한 값에 대한 예측 가격:</h3>
<ul id="predictions-list"></ul>
</div>
</div>
<script src="tf4.mjs"></script>
</body>
</html>tf4.mjs
let model; // 전역 변수로 학습된 모델을 저장하여 나중에 접근 가능하도록 설정
// 주택 데이터셋을 가져오는 함수 (비동기 함수로 fetch를 사용)
async function fetchHousingData() {
const response =
await fetch('https://raw.githubusercontent.com/selva86/datasets/master/BostonHousing.csv');
const data = await response.text();
const rows = data.split('\n').slice(1).filter(row => row.length > 0);
const parsedData = rows.map(row => {
const cols = row.split(',');
return {
crim: parseFloat(cols[0]), // 범죄율 (CRIM)
rm: parseFloat(cols[5]), // 방 개수 (RM)
lstat: parseFloat(cols[12]), // 저소득층 비율 (LSTAT)
medv: parseFloat(cols[13]) // 중간 주택 가격 (MEDV)
};
});
return parsedData;
}
// 다중회귀 모델을 학습시키고, 예측 결과를 표시하는 메인 함수
async function run() {
// 로딩 메시지를 표시
document.getElementById('loading-message').style.display = 'block';
const data = await fetchHousingData();
const dataX = data.map(d => [d.crim, d.rm, d.lstat]); // CRIM, RM, LSTAT 값을 입력 데이터로 추출
const dataY = data.map(d => d.medv); // MEDV 값을 출력 데이터로 추출
const tensorX = tf.tensor2d(dataX, [dataX.length, 3]); // 입력 데이터를 2D 텐서로 변환 (행: 샘플 수, 열: 독립변수 수)
const tensorY = tf.tensor2d(dataY, [dataY.length, 1]); // 출력 데이터를 2D 텐서로 변환
model = tf.sequential();
model.add(tf.layers.dense({
units: 1,
inputShape: [3],
kernelInitializer: 'zeros', // 가중치 초기화를 추가
biasInitializer: 'zeros' // 편향 초기화를 추가
}));
// 학습률을 명시적으로 설정
model.compile({loss: 'meanSquaredError', optimizer: tf.train.sgd(0.001)});
await model.fit(tensorX, tensorY, {
epochs: 500,
batchSize: 32, // 배치 사이즈 추가
shuffle: true // 데이터를 셔플하여 학습
});
const predictions = model.predict(tensorX).dataSync(); // 학습된 모델로 예측 수행, 결과를 동기적으로 가져옴
displayPredictions(dataY, predictions); // 실제 값과 예측 값을 리스트로 표시
// 로딩 메시지를 숨김
document.getElementById('loading-message').style.display = 'none';
document.getElementById('result-container').style.display = 'block'; // 결과 컨테이너를 화면에 표시
}
// 실제 값과 예측 값을 리스트로 표시하는 함수
function displayPredictions(actualValues, predictions) {
const predictionsList = document.getElementById('predictions-list');
predictionsList.innerHTML = ''; // 기존 리스트 초기화
predictions.forEach((pred, index) => {
const listItem = document.createElement('li');
listItem.textContent = `실제값: ${actualValues[index].toFixed(2)}, 예측값: ${pred.toFixed(2)}`;
predictionsList.appendChild(listItem);
});
}
// 입력된 값을 바탕으로 예측 가격을 계산하고 표시하는 함수
function predictPrice() {
const crimInput = parseFloat(document.getElementById('crimInput').value);
const roomsInput = parseFloat(document.getElementById('roomsInput').value);
const lstatInput = parseFloat(document.getElementById('lstatInput').value);
if (!isNaN(crimInput) && !isNaN(roomsInput) && !isNaN(lstatInput) && model) {
const inputTensor = tf.tensor2d([[crimInput, roomsInput, lstatInput]], [1, 3]); // 입력 값을 2D 텐서로 변환
let prediction = model.predict(inputTensor).dataSync()[0]; // 모델을 사용하여 가격 예측 수행
if (prediction < 0) {
prediction = 0; // 예측값이 음수인 경우 0으로 제한
}
document.getElementById('singlePrediction').textContent =
`예측된 가격: ${prediction.toFixed(2)}`; // 예측 결과를 화면에 표시
} else {
// 모든 값을 입력하지 않은 경우 경고 메시지 표시
document.getElementById('singlePrediction').textContent = '모든 값을 입력해주세요!';
}
}
// 버튼 클릭 이벤트 리스너 추가
document.getElementById('showButton').addEventListener('click', run); // 버튼 클릭 시 run 함수 실행
document.getElementById('predictButton').addEventListener('click', predictPrice); // '예측가격 확인' 버튼 클릭 시 predictPrice 함수 실행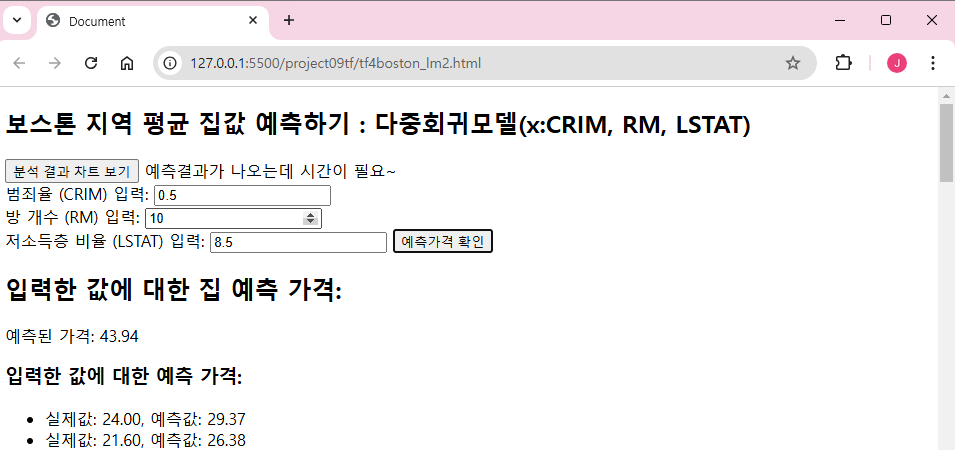
분류 실습 (아이리스)
이항 분류(찬/반, 남/여, 더워/추워, ...) 시그모이드 함수 사용
> y = wx + b의 결과로 나온 수치를 시그모이드 함수를 써서 0~1 사이의 실수값으로 변환하고
0.5를 기준으로 0.5 이상은 1, 이하는 0으로 나눈다.
다항 분류(상/중/하, A/B/C, ...) 소프트맥스 함수 사용
> 상중하의 경우 0 || 1 || 2 나눌 수 있지만 배열로 나는 것이 좋다.
1 0 0 || 0 1 0 || 0 0 1 (원-핫인코딩 : 문자열을 1차열 배열로 바꿔주는 인코딩)
tf5iris.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/@tensorflow/tfjs/dist/tf.min.js"></script>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/@tensorflow/tfjs-vis/dist/tfjs-vis.umd.min.js"></script>
<style>
#input-container {
margin-top: 20px;
}
#prediction-result {
margin-top: 20px;
font-size: 18px;
font-weight: bold;
color: blue;
}
#loading-message {
display: none; /* 초기에는 숨김 */
font-weight: bold;
color: #007bff;
margin: 20px 0;
}
#chart-container {
margin-top: 30px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Iris Dataset으로 분류</h1>
<p>TensorFlow.js를 사용하여 Iris 데이터셋을 분류하고, 산점도 시각화</p>
<button id="trainModel">모델 학습 시작</button>
<div id="loading-message">분류 모델 생성 중 ...</div>
<p id="trainingStatus"></p>
<div id="input-container">
<h3>분류를 위한 꽃 특성 입력:</h3>
Sepal Length:</label>
<input type="number" id="sepalLength" step="0.1" /><br>
Sepal Width:</label>
<input type="number" id="sepalWidth" step="0.1" /><br>
Petal Length:</label>
<input type="number" id="petalLength" step="0.1" /><br>
Petal Width:</label>
<input type="number" id="petalWidth" step="0.1" /><br>
<button id="predictButton">분류 결과 확인</button>
</div>
<p id="prediction-result"></p>
<div id="chart-container">
<div id="scatter-plot"></div>
</div>
<script type="module" src="./tf5iris.mjs"></script>
</body>
</html>
연습용 dataset
iris : https://raw.githubusercontent.com/mwaskom/seaborn-data/master/iris.csv
데이터 읽기 확인
const IRIS_URL = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/mwaskom/seaborn-data/master/iris.csv";
let model;
async function loadData() {
const response = await fetch(IRIS_URL);
const data = await response.text();
console.log(data);
}
features data push / labels one-hot encoding
const IRIS_URL = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/mwaskom/seaborn-data/master/iris.csv";
let model;
async function loadData() {
... 생략
const lines = data.split("\n").slice(1); // 첫번째 행 제거
const features = []; // features : 독립변수
const labels = []; // labels : 종속변수
lines.forEach(line => {
const [sepalLength,sepalWidth,petalLength,petalWidth,species] = line.split(",");
if(!species) return; // 마지막 빈 줄 건너뛰기
features.push([parseFloat(sepalLength), parseFloat(sepalWidth), parseFloat(petalLength), parseFloat(petalWidth)]);
// 꽃의 종류 : setosa, versicolor, virginica
// One-hot Encoding
if(species === 'setosa') labels.push([1,0,0]);
else if(species === 'versicolor') labels.push([0,1,0]);
else if(species === 'virginica') labels.push([0,0,1]);
});
//console.log(features);
//console.log(labels);
return {
features:tf.tesnsor2d(features),
labels:tf.tesnsor2d(labels),
}
}

독립변수에 데이터 푸쉬 One-hot Encoding
모델 학습 및 시각화
async function trainModel() {
// 로딩 메세지 표시
document.getElementById("loading-message").style.display = "block";
const data = await loadData();
// 텐서를 배열로 반환
const featuresArray = await data.features.array(); // arraySync() 해줘도 괜찮음, 비동기 배열 반환
const labelsArray = await data.labels.array();
data.features.dispose();
data.labels.dispose();
// 모델
model = tf.sequential();
model.add(
tf.layers.dense({ inputShape: [4], units: 16, activation: "relu" })
); // units에는 일반적으로 4의 배수로 많이 준다.
//model.add(tf.layers.dense({units:24, activation:'relu'}));
//model.add(tf.layers.dense({units:16, activation:'relu'}));
// 4개가 16개로 들어오고 빠져나감, 다시 24개로 들어오고 빠져나감, 16개, 마지막에 3개로 빠져나감
model.add(tf.layers.dense({ units: 3, activation: "softmax" }));
model.compile({
loss: "categoricalCrossentropy",
optimizer: tf.train.adam(),
metrics: ["accuracy"],
});
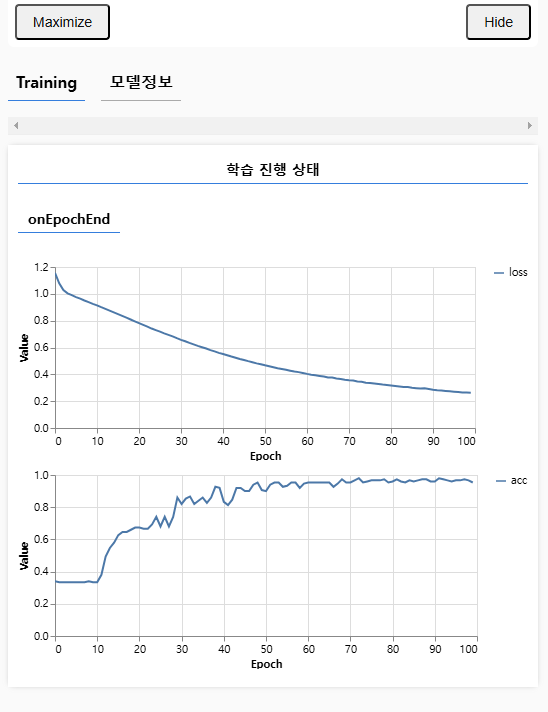
// 시각화
const metricsContainer = {
name: "학습 진행 상태",
tab: "Training",
};
const callbacks = tfvis.show.fitCallbacks(metricsContainer, ["loss", "acc"], {
height: 200,
callbacks: ["onEpochEnd"],
});
// 모델 학습, 컴파일할 때 metrics를 써주면 모델이 알아서 history를 준다.
const history = await model.fit(
tf.tensor2d(featuresArray),
tf.tensor2d(labelsArray),
{
epochs: 100,
batchSize: 16,
verbose: 1,
callbacks: callbacks, // tfvis 콜백 추가가
}
);
console.log(history.history);
document.getElementById(
"trainingStatus"
).innerText = `모델 학습 완료(정확도:${(
history.history.acc.slice(-1)[0] * 100
).toFixed(2)}%)`;
// 로딩 메세지 숨기기
document.getElementById("loading-message").style.display = "none";
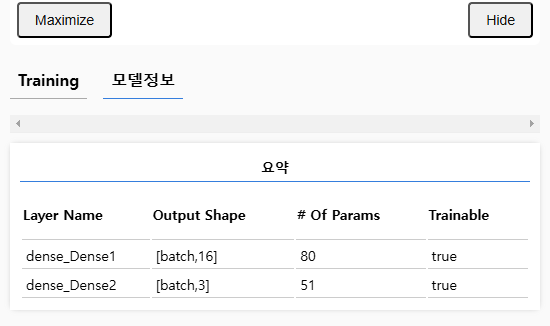
// 모델 정보 시각화
tfvis.show.modelSummary({ name: "요약", tab: "모델정보" }, model);
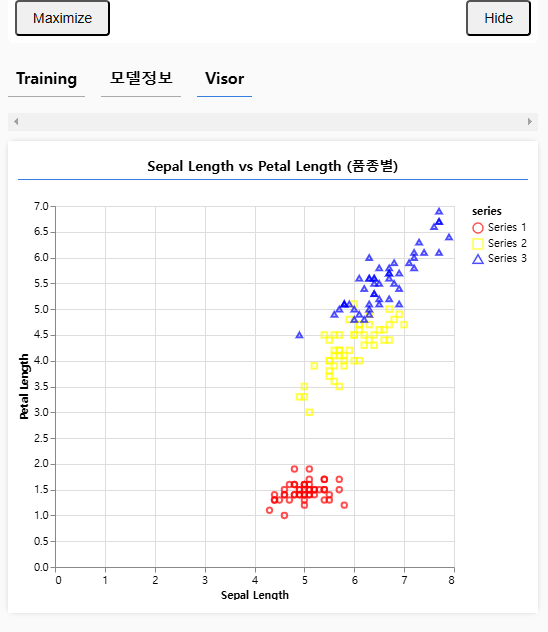
// 산점도 시각화
visualizeScatterPlot(featuresArray, labelsArray);
}function visualizeScatterPlot(featuresArray, labelsArray) {
const classes = ["setosa", "versicolor", "virginica"];
// 각 품종별 데이터 분리
const seriesData = classes.map((className, classIndex) => {
const values = featuresArray
.map((feature, i) => {
const label = labelsArray[i].indexOf(1); // One-hot에서 클래스 인덱스 가져오기
if (label === classIndex) {
return { x: feature[0], y: feature[2] }; // Sepal Length vs Petal Length
}
return null;
})
.filter((point) => point !== null); // 유효한 데이터만 필터링
return { name: className, values }; // 시리즈 생성
});
// 시리즈 데이터와 색상 매핑의 길이를 검증
console.log("Series Data:", seriesData);
// Scatter Plot 렌더링
tfvis.render.scatterplot(
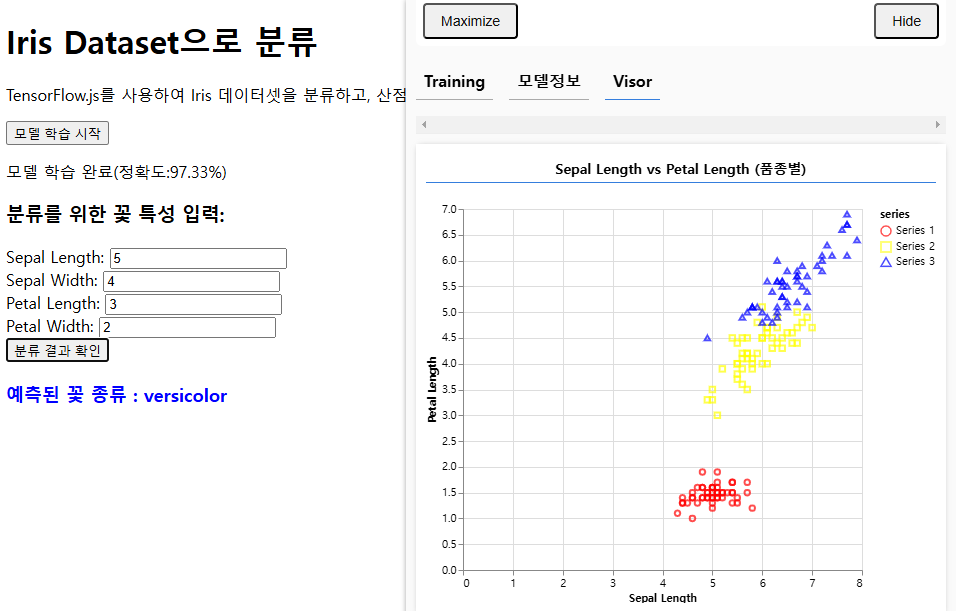
{ name: "Sepal Length vs Petal Length (품종별)" },
{ values: seriesData.map((series) => series.values) }, // 데이터 시리즈의 values만 전달
{
xLabel: "Sepal Length",
yLabel: "Petal Length",
height: 400,
seriesColors: ["red", "yellow", "blue"], // 각 시리즈에 대해 색상 지정
}
);
}
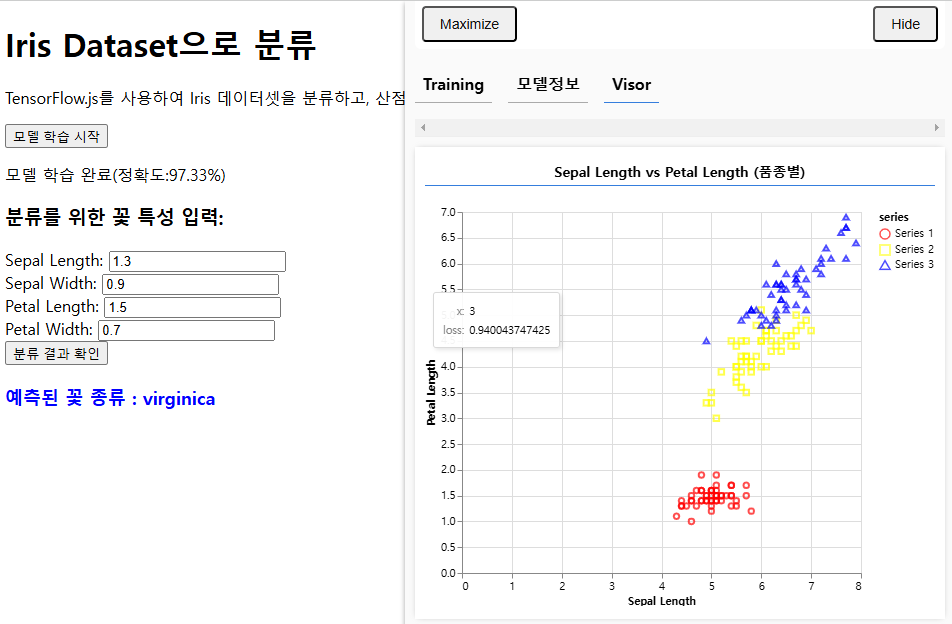
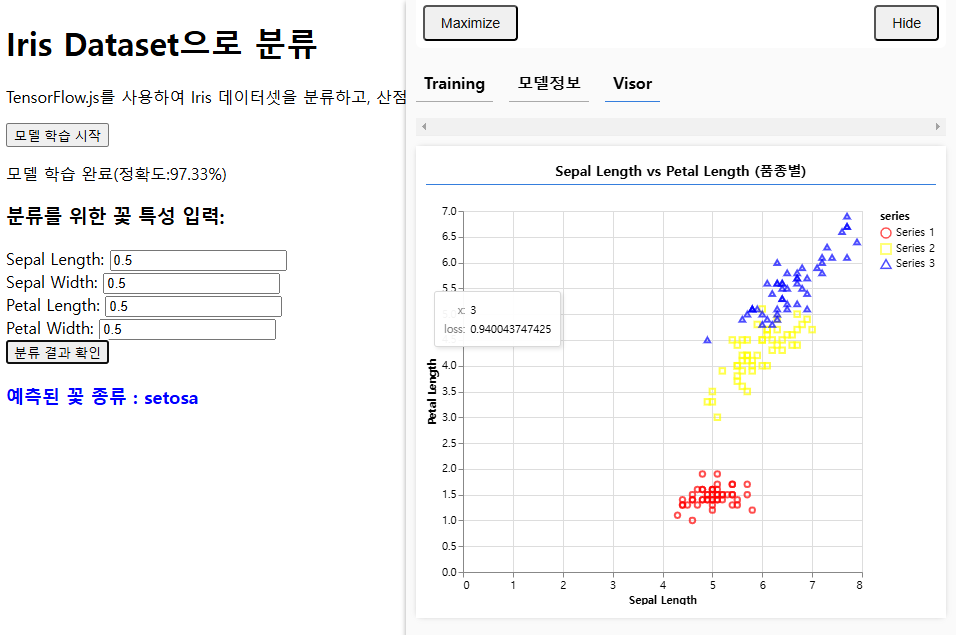
예측된 꽃 종류 분류
async function predictSpecies() {
if(!model) {
alert("모델이 학습되지 않음, 모델 학습 시작 버튼 클릭");
return;
}
// 입력값 얻기
const sepalLength = parseFloat(document.getElementById('sepalLength').value);
const sepalWidth = parseFloat(document.getElementById('sepalWidth').value);
const petalLength = parseFloat(document.getElementById('petalLength').value);
const petalWidth = parseFloat(document.getElementById('petalWidth').value);
const inputTensor = tf.tensor2d([[sepalLength, sepalWidth, petalLength, petalWidth]]);
const prediction = model.predict(inputTensor);
const predictedIndex = prediction.argMax(-1).dataSync()[0];
inputTensor.dispose();
let species;
if(predictedIndex === 0) species = 'setosa';
else if(predictedIndex === 1) species = 'versicolor';
else if(predictedIndex === 2) species = 'virginica';
document.getElementById("prediction-result").innerText = `예측된 꽃 종류 : ${species}`;
}
tf5iris.mjs
const IRIS_URL =
"https://raw.githubusercontent.com/mwaskom/seaborn-data/master/iris.csv";
let model;
async function loadData() {
const response = await fetch(IRIS_URL);
const data = await response.text();
//console.log(data);
const lines = data.split("\n").slice(1); // 첫번째 행 제거
const features = []; // features : 독립변수
const labels = []; // labels : 종속변수
lines.forEach((line) => {
const [sepalLength, sepalWidth, petalLength, petalWidth, species] =
line.split(",");
if (!species) return; // 마지막 빈 줄 건너뛰기
features.push([
parseFloat(sepalLength),
parseFloat(sepalWidth),
parseFloat(petalLength),
parseFloat(petalWidth),
]);
// 꽃의 종류 : setosa, versicolor, virginica
// One-hot Encoding
if (species === "setosa") labels.push([1, 0, 0]);
else if (species === "versicolor") labels.push([0, 1, 0]);
else if (species === "virginica") labels.push([0, 0, 1]);
});
//console.log(features);
//console.log(labels);
return {
features: tf.tensor2d(features),
labels: tf.tensor2d(labels),
};
}
async function trainModel() {
// 로딩 메세지 표시
document.getElementById("loading-message").style.display = "block";
const data = await loadData();
// 텐서를 배열로 반환
const featuresArray = await data.features.array(); // arraySync() 해줘도 괜찮음, 비동기 배열 반환
const labelsArray = await data.labels.array();
data.features.dispose();
data.labels.dispose();
// 모델
model = tf.sequential();
model.add(
tf.layers.dense({ inputShape: [4], units: 16, activation: "relu" })
); // units에는 일반적으로 4의 배수로 많이 준다.
//model.add(tf.layers.dense({units:24, activation:'relu'}));
//model.add(tf.layers.dense({units:16, activation:'relu'}));
// 4개가 16개로 들어오고 빠져나감, 다시 24개로 들어오고 빠져나감, 16개, 마지막에 3개로 빠져나감
model.add(tf.layers.dense({ units: 3, activation: "softmax" }));
model.compile({
loss: "categoricalCrossentropy",
optimizer: tf.train.adam(),
metrics: ["accuracy"],
});
// 시각화
const metricsContainer = {
name: "학습 진행 상태",
tab: "Training",
};
const callbacks = tfvis.show.fitCallbacks(metricsContainer, ["loss", "acc"], {
height: 200,
callbacks: ["onEpochEnd"],
});
// 모델 학습, 컴파일할 때 metrics를 써주면 모델이 알아서 history를 준다.
const history = await model.fit(
tf.tensor2d(featuresArray),
tf.tensor2d(labelsArray),
{
epochs: 100,
batchSize: 16,
verbose: 1,
callbacks: callbacks, // tfvis 콜백 추가
}
);
console.log(history.history);
document.getElementById(
"trainingStatus"
).innerText = `모델 학습 완료(정확도:${(
history.history.acc.slice(-1)[0] * 100
).toFixed(2)}%)`;
// 로딩 메세지 숨기기
document.getElementById("loading-message").style.display = "none";
// 모델 정보 시각화
tfvis.show.modelSummary({ name: "요약", tab: "모델정보" }, model);
// 산점도 시각화
visualizeScatterPlot(featuresArray, labelsArray);
}
async function predictSpecies() {
if(!model) {
alert("모델이 학습되지 않음, 모델 학습 시작 버튼 클릭");
return;
}
// 입력값 얻기
const sepalLength = parseFloat(document.getElementById('sepalLength').value);
const sepalWidth = parseFloat(document.getElementById('sepalWidth').value);
const petalLength = parseFloat(document.getElementById('petalLength').value);
const petalWidth = parseFloat(document.getElementById('petalWidth').value);
const inputTensor = tf.tensor2d([[sepalLength, sepalWidth, petalLength, petalWidth]]);
const prediction = model.predict(inputTensor);
const predictedIndex = prediction.argMax(-1).dataSync()[0];
inputTensor.dispose();
let species;
if(predictedIndex === 0) species = 'setosa';
else if(predictedIndex === 1) species = 'versicolor';
else if(predictedIndex === 2) species = 'virginica';
document.getElementById("prediction-result").innerText = `예측된 꽃 종류 : ${species}`;
}
function visualizeScatterPlot(featuresArray, labelsArray) {
const classes = ["setosa", "versicolor", "virginica"];
// 각 품종별 데이터 분리
const seriesData = classes.map((className, classIndex) => {
const values = featuresArray
.map((feature, i) => {
const label = labelsArray[i].indexOf(1); // One-hot에서 클래스 인덱스 가져오기
if (label === classIndex) {
return { x: feature[0], y: feature[2] }; // Sepal Length vs Petal Length
}
return null;
})
.filter((point) => point !== null); // 유효한 데이터만 필터링
return { name: className, values }; // 시리즈 생성
});
// 시리즈 데이터와 색상 매핑의 길이를 검증
console.log("Series Data:", seriesData);
// Scatter Plot 렌더링
tfvis.render.scatterplot(
{ name: "Sepal Length vs Petal Length (품종별)" },
{ values: seriesData.map((series) => series.values) }, // 데이터 시리즈의 values만 전달
{
xLabel: "Sepal Length",
yLabel: "Petal Length",
height: 400,
seriesColors: ["red", "yellow", "blue"], // 각 시리즈에 대해 색상 지정
}
);
}
document.getElementById("trainModel").addEventListener("click", trainModel);
document.getElementById("predictButton").addEventListener("click", predictSpecies);가상화(Virtualization)
💡 가상화란?
서버, 스토리지, 네트워크 및 기타 물리적 시스템에 대한 가상 표현을 생성하는 데 사용할 수 있는 기술이며, 가상 소프트웨어는 물리적 하드웨어 기능을 모방하여 하나의 물리적 머신에서 여러 가상 시스템을 동시에 실행한다.
서버당 1개의 컴퓨터가 필요하다. 예를 들어 3개의 서버를 운영할 때 Bare Metal(OS만 깔려있는 것, 물리적인 컴퓨터) 윈도우, 맥, 리눅스 운영체제의 컴퓨터를 사용한다고치면 현실적으로 금전적, 공간적으로 어려운 부분이 있다.
그래서 한대의 컴퓨터에 가상화(Virtualization)를 할 수 있는 프로그램을 깔아두고 별도의 독립적인 컴퓨터가 있는 것처럼 가상의 컴퓨터를 운영할 수 있다. 램의 용량이 크다면 여러개의 가상화한 서버를 둘 수 있다.
가상화를 할 수 있게해주는 하이퍼바이저 프로그램을 사용한다.
하이퍼바이저를 사용하지 않고도 시스템으로 직접 만들 수도 있다. (AWS)
AWS도 가상화된 서버를 임대를 해주는 것 (리눅스 서버임)
하이퍼바이저 프로그램을 설치하고 가상화 시스템을 만들고 리눅스를 설치하고 리눅스 공부를 해보자!
하이퍼바이저 프로그램 : VMware, VirtualBox, Microsoft Hyper-V 등.
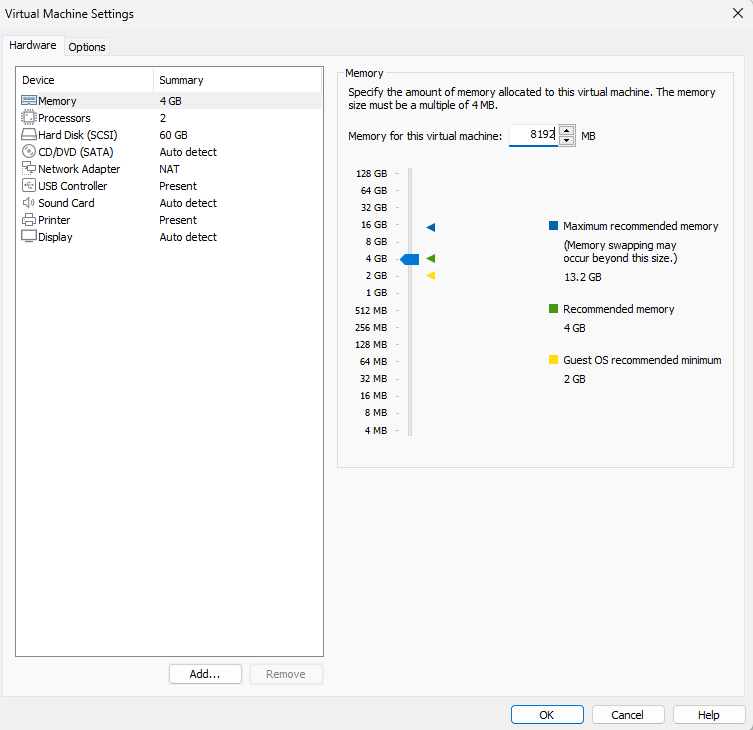
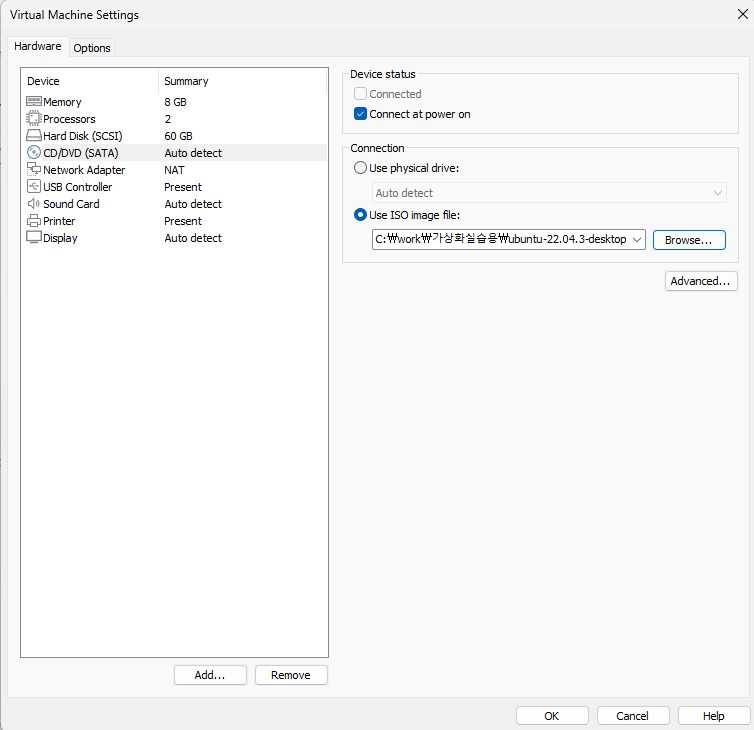
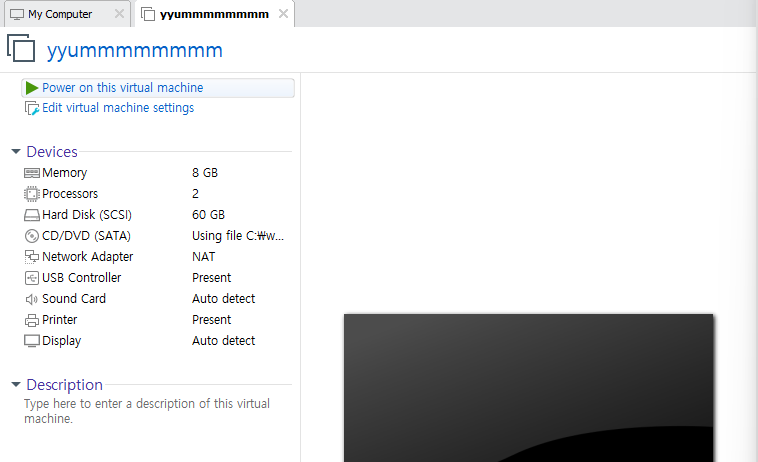
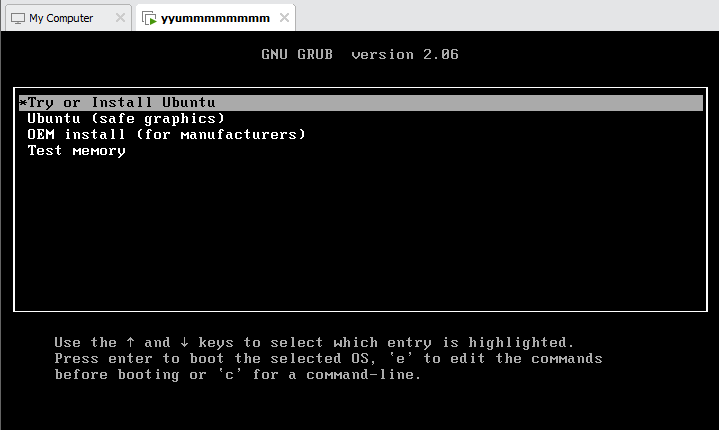
하이퍼바이저 설치
vmware-workstation17.exe
관리자 권한으로 실행, 기본 옵션으로 계속 next 하고 install
무료버전으로 사용, skip this version


'Study > Acorn' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 241217 가상화 (하이퍼바이저 프로그램 배포, AWS 실습) (1) | 2024.12.17 |
|---|---|
| 241216 리눅스 (기본 명령어, Java, MariaDB 설치) (0) | 2024.12.16 |
| 241212 데이터 분석 (단순 선형 회기분석) (0) | 2024.12.12 |
| 241211 노드 (RESTful DB연동, 데이터 분석 : TensorFlow.js) (0) | 2024.12.11 |
| 241210 노드 (RESTful DB 연동) (0) | 2024.12.10 |


